Harnessing the power of artificial intelligence in leukemia diagnosis
Groundbreaking study presents a new way to predict genetic aberrations, bringing hope to leukemia patients
In a remarkable breakthrough, researchers from the University of Münster and the University Hospital Münster in Germany have unveiled an innovative method that utilizes artificial intelligence (AI) to predict important genetic features of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). This cutting-edge approach holds immense potential for revolutionizing the field of diagnostics and guiding targeted treatments at an early stage, offering renewed hope to those battling this highly aggressive form of leukemia.
To effectively treat AML patients, timely access to genetic information is crucial. However, conventional genetic testing can be both expensive and time-consuming, resulting in a significant gap between diagnosis and the availability of critical genetic data. This gap has led a team of IT specialists and physicians to develop a transformative solution that could bridge this divide.
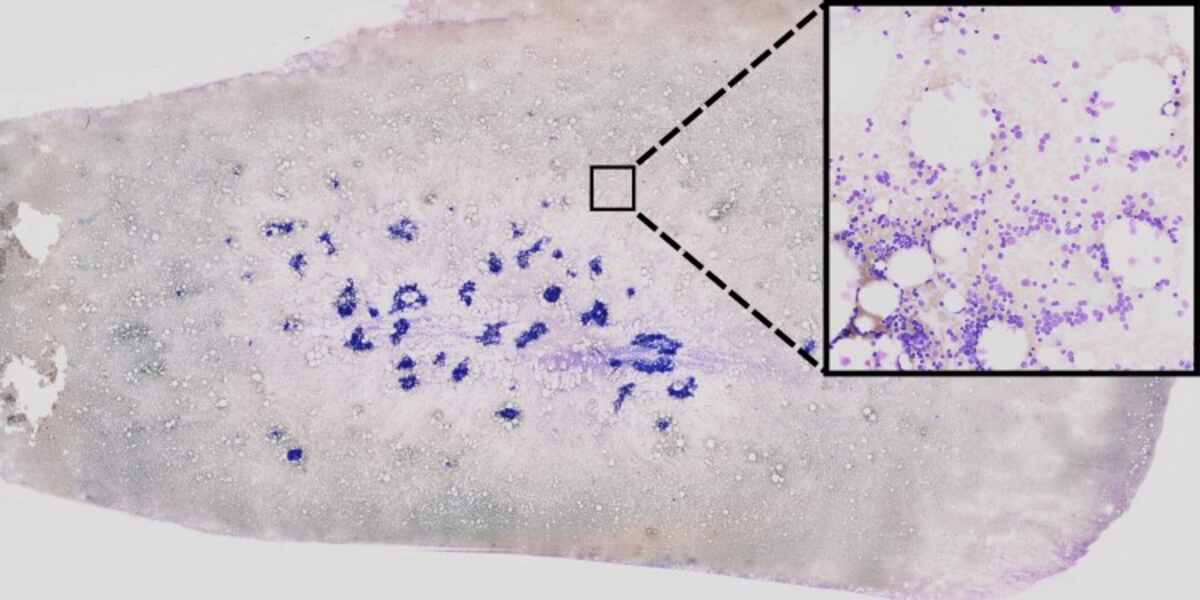
Published in the esteemed journal "Blood Advances," their study showcases how AI, combined with high-resolution microscopic images of bone marrow smears, can accurately predict various genetic aberrations. The team extracted genetic information from massive datasets, comprising multi-gigabyte scans from over 400 AML patients. These high-resolution images, with pixel sizes of 270,000 by 135,000 on average, provided the necessary foundation for the deep learning algorithms.
Under the leadership of Prof. Benjamin Risse, the team developed a groundbreaking deep-learning method that enables the automatic recognition of genetic features and intricate patterns present in cytological images. The algorithm effectively categorizes different cell types and identifies genetic aberrations that may elude human observers. The AI system's exceptional sensitivity allows it to detect faint patterns and hidden textures that would typically go unnoticed by the human eye.
What sets this method apart is its end-to-end AI pipeline, unifying unsupervised, self-supervised, and supervised learning processes. The integration of these approaches significantly reduces manual preliminary work, providing real-time monitoring of results. When faced with problematic cell images, the AI system works in synergy with human experts to ensure accuracy, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the diagnostic process.
While this groundbreaking method cannot replace genetic analyses, it serves as a vital tool in the early stages of diagnosis for leukemia patients. For individuals with aggressive forms of the disease, who cannot afford delays associated with complete genetic analyses, this approach offers crucial insights into the underlying genetic abnormalities.
The implications of this study reach beyond leukemia treatment. The researchers envision a future where digital methods and artificial intelligence play an increasingly pivotal role in analyzing large medical datasets. The ability to make personalized treatment recommendations for patients with malignant diseases could be revolutionized, laying the groundwork for similar breakthroughs in the diagnosis of other bone marrow disorders.
The research project received funding from the European Union and the German Research Foundation, highlighting the collaborative efforts and dedication of the scientific community in combating complex medical challenges.
It is inspiring to witness how AI and cutting-edge technology are transforming the landscape of medical diagnostics. With every breakthrough, we inch closer to personalized and targeted treatment strategies that offer hope, strength, and ultimately, a brighter future for patients facing daunting health battles.

 How to resolve AdBlock issue?
How to resolve AdBlock issue?