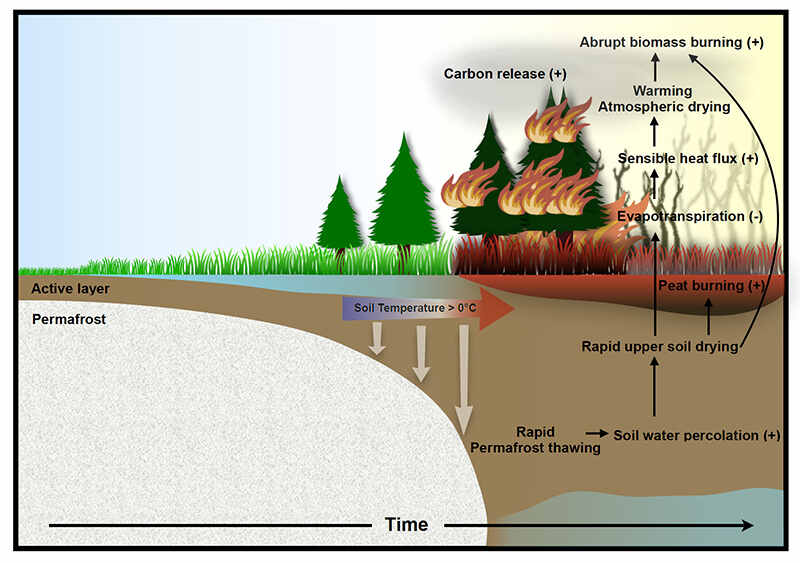
The article provides a detailed analysis of the sudden intensification of northern wildfires due to future permafrost thawing in the Subarctic and Arctic regions. Published in the journal Nature Communications by an international team of climate scientists and permafrost experts, this study sheds light on the potential consequences of global warming on permafrost thawing and its direct correlation with an increase in wildfires. The groundbreaking research incorporates new climate computer model simulations that underscore the urgency of addressing the impact of accelerated permafrost thawing on wildfire occurrences.
A crucial aspect highlighted in the article is the use of cutting-edge technology to facilitate this research. The study leverages the capabilities of one of the most comprehensive earth system models, the Community Earth System Model, to simulate the intricate relationship between permafrost, soil water, and wildfires. Such advanced modeling techniques, including 50 past-to-future simulations conducted on the IBS supercomputer Aleph, have enabled a more accurate representation of the complex interplay between anthropogenic factors, permafrost thawing, and wildfire intensification.
Furthermore, the research emphasizes the significance of integrating diverse perspectives and expertise to address the challenges posed by climate change comprehensively. Collaborations between scientists from the IBS Center for Climate Physics in Busan, South Korea, and the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colorado, attest to the global effort required to tackle climate-related issues effectively. Additionally, contributions from various co-authors representing the Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Pusan National University further enrich the study by bringing in multifaceted insights and expertise.
The findings of the study serve as a critical wake-up call to policymakers, scientists, and the broader community to prioritize collective action toward mitigating the adverse effects of climate change. The projected scenarios of extensive permafrost thawing, coupled with the heightened risk of wildfires in high-latitude regions, underscore the urgent need for proactive measures and sustainable environmental practices.
In conclusion, the research detailed in the article not only underscores the intrinsic link between permafrost thawing and wildfire intensification but also highlights the crucial role played by advanced computational capabilities, exemplified by the IBS supercomputer Aleph, in advancing our understanding of complex climatic phenomena. By synergizing diverse perspectives and cutting-edge technology, we can pave the way for informed decision-making and concerted efforts to combat the escalating threats posed by climate change. For further information, please refer to the original publication: "Abrupt increase in Arctic-Subarctic wildfires caused by future permafrost thaw" (Nature Communications, 2024).


 How to resolve AdBlock issue?
How to resolve AdBlock issue?