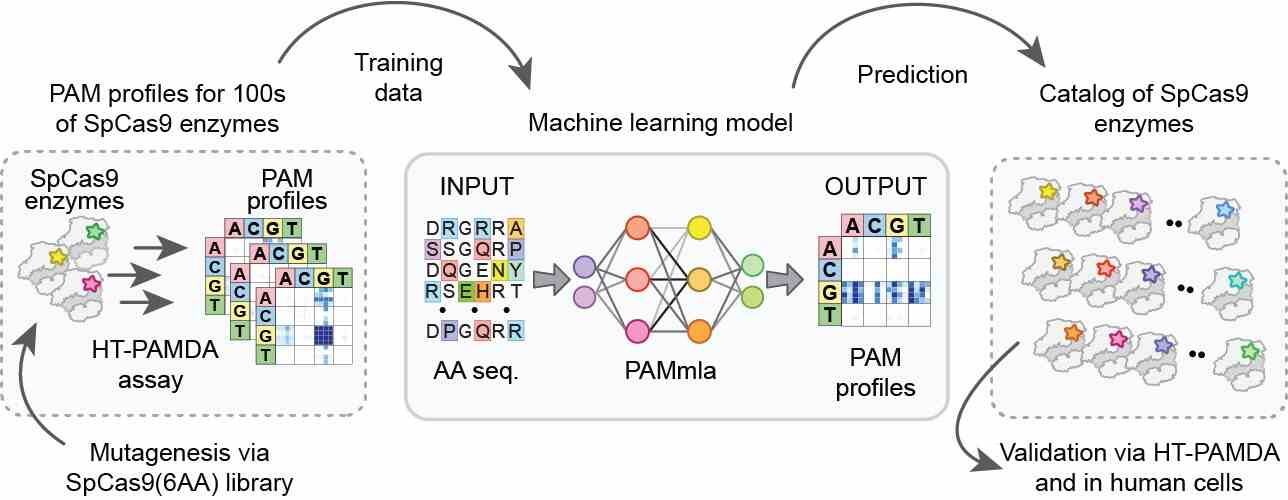
In a remarkable convergence of artificial intelligence and biotechnology, researchers at Mass General Brigham have introduced a groundbreaking method for engineering "bespoke enzymes" specifically designed for gene editing. This innovative approach utilizes machine learning to create enzymes with unprecedented precision, potentially revolutionizing treatments for a wide range of genetic disorders.
The Quest for Precision
Gene editing has long been recognized as a leading frontier in modern medicine, offering the promise of correcting genetic anomalies at their source. However, a significant challenge has always been ensuring specificity—ensuring that edits occur exactly where intended, without any off-target effects. Traditional enzymes used in gene editing, while effective, often lack the level of precision required for such meticulous tasks.
This is where machine learning comes into play. By training algorithms on extensive datasets of enzyme structures and functions, the research team has developed models capable of predicting and designing enzyme variants with improved specificity. These custom-designed enzymes can precisely target genetic sequences, minimizing unintended alterations.
A Symphony of Science and Technology
Dr. Rachel A. Silverstein, the principal investigator of the study, stated, "This is a paradigm shift. By integrating machine learning into enzyme design, we're not just refining existing tools—we're creating entirely new instruments for gene editing."
The implications of this technology are profound. It could lead to more effective and safer treatments for conditions such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and certain types of cancer. Additionally, the adaptability of this approach means it can be customized to fit individual genetic profiles, paving the way for an era of personalized medicine.
Looking Ahead
Although the research is still in its early stages, the results are promising. The team is now focusing on refining the algorithms and conducting preclinical trials to evaluate the efficacy and safety of these bespoke enzymes in living organisms.
Dr. Ben Kleinstiver, a co-author of the study, emphasized the collaborative nature of the project: "This achievement is the culmination of interdisciplinary efforts, bringing together experts in computational biology, genetics, and molecular engineering."
As the lines between biology and technology continue to blur, innovations like this underscore the transformative potential of interdisciplinary research. The intersection of machine learning and gene editing not only showcases scientific ingenuity but also offers hope for countless individuals affected by genetic diseases.


 How to resolve AdBlock issue?
How to resolve AdBlock issue?